How much do you know about stroboscopic? Common misunderstanding analysis
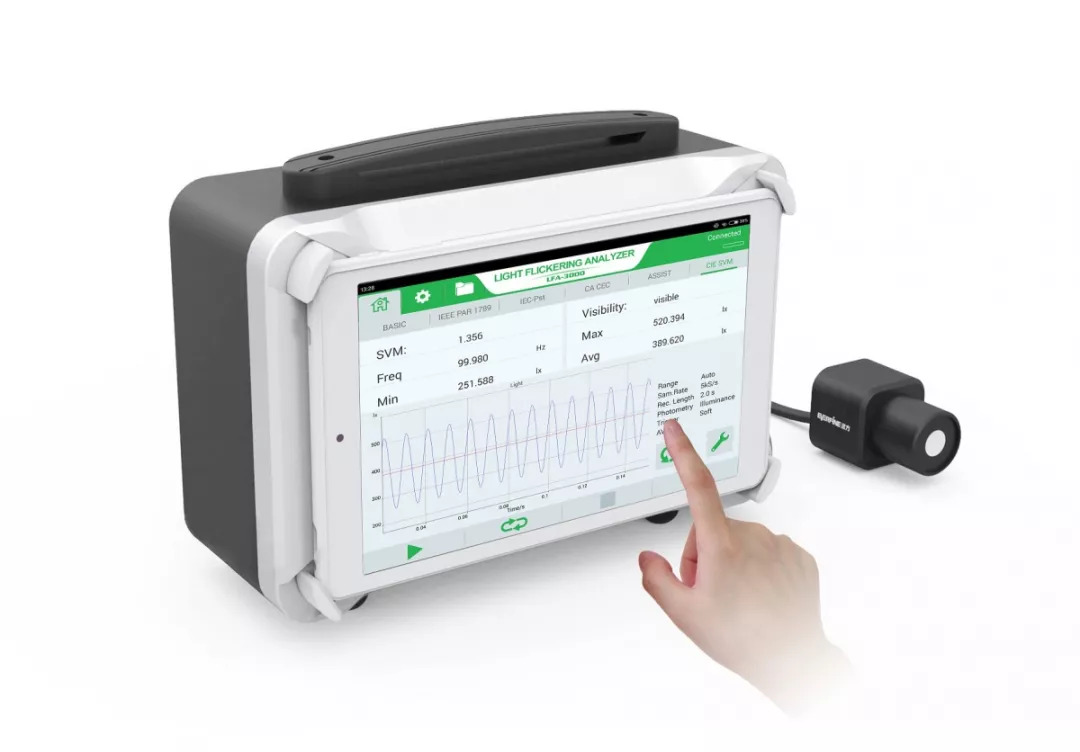
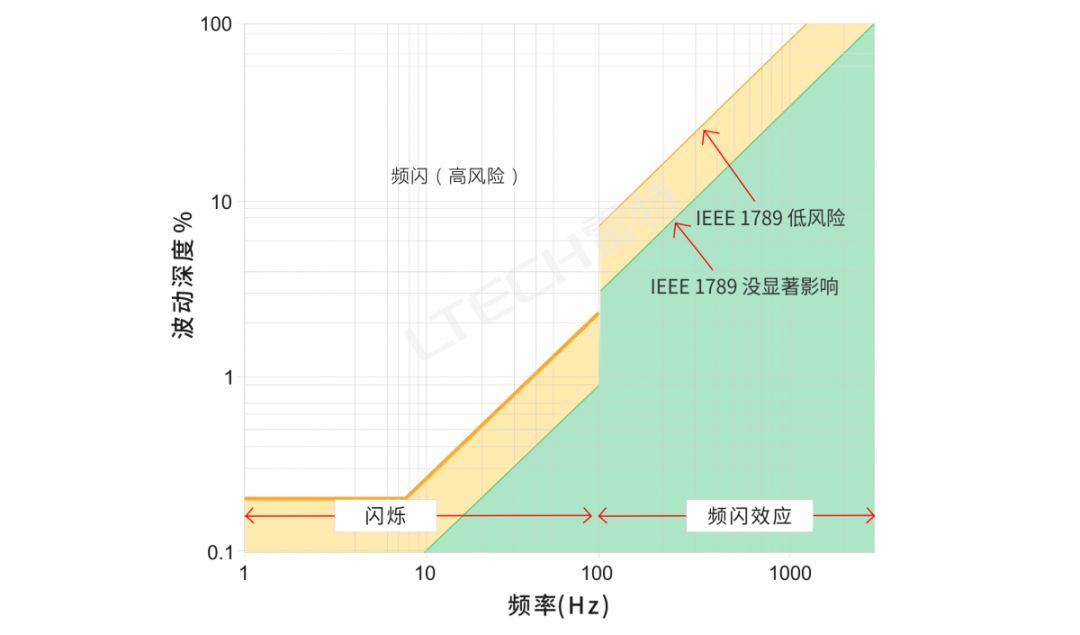
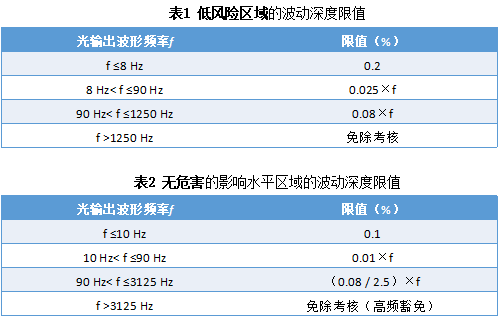
Lighting strobe is not totally negative in life 01 In addition to the annoying flicker caused by lighting, the flickering light can also cause some serious diseases, such as headaches, visual impairment, or in extreme cases, seizures. Even if the flicker is slight, such as at a high frequency of 100 to 150 Hz, your eyes may not consciously look at it, but the brain can still detect and react to it, which may bring negative consequences. In particular, athletes of stadiums and warehouse workers are more prone to accidents under poor lighting conditions, which may cause a stroboscopic effect. However, in real life, there are still cases related to flicker. These are the "flickers" we want: ◎Lights on ambulances, fire engines and police cars ◎Wing indicator light when the plane is landing ◎Laser lights for concerts and bars In addition, there are also foreign scientific researches that control the flashing of lights to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD). Almost all types of lamps are prone to flicker, including incandescent lamps, halogen lamps, and even LED bulbs. But the effect of each light is different. For example, in incandescent lamps and halogen lamps, the filament temperature reacts slowly to changes in current, so you won't notice the effect of flickering. For the current changes, the LED responds almost immediately, so the flickering will be more noticeable. At present, the stroboscopic index is commonly used to describe the stroboscopic degree of the light source, the comprehensive stroboscopic percentage and two other variables: light waveform and duty cycle. Among them, the stroboscopic percentage is equal to the difference between the maximum light output and the minimum light output in a switching period divided by the sum of the maximum light output and the minimum light output, and the stroboscopic index is equal to the amount of exceeding the average light output in a switching period divided by the total light output . The lower the stroboscopic percentage (depth of fluctuation) and the stroboscopic index, the less the light source flickers or causes the stroboscopic effect. ▲Figure 1 Strobe of various light sources It can be seen from Figure 1 that due to the use of inductive ballasts and electronic ballasts, the double-U compact fluorescent lamp has a significant difference in stroboscopic percentage, which shows that lighting appliances have a great influence on stroboscopic. In the same situation, the LED will produce heavy stroboscopic, but it is also due to the selection of a bad LED driver, which has nothing to do with the LED lamp itself. Regarding stroboscopic, there are different definitions and different reference indicators, such as IEEE, Energy Star, IEC, CIE, etc. Here are the definitions of two organizations: (1) CIE (Commission Internationale de L'Eclairage) CIE 17.443 e-ILV: Temporal Light Artefacts (TLA): In a specific environment, light stimuli whose brightness or spectrum fluctuates over time cause changes in the observer's visual perception. The flicker, stroboscopic effect and phantom effect below are all different types of TLA. Definition in CIE TN006-2016: ◎Flicker : For static observers in a static environment, the perception of visual instability caused by light stimuli whose brightness or spectral distribution fluctuates over time. Unlike the "flicker" and "brightness changes over time" we mentioned in the past, the environment and observers here are static. ◎Stroboscopic effect: For static observers in a non-static environment (moving objects), changes in the perception of motion caused by light stimuli whose brightness or spectrum fluctuates over time. For example, under the periodically fluctuating brightness of a square wave, a continuously moving target will be perceived as discontinuous movement; if the brightness fluctuation period is consistent with the target rotation period, the target will be regarded as stationary. ◎The phantom array effect: also known as ghost, for non-static observers in a static environment, the perception of the shape or spatial position of an object caused by light stimuli whose brightness or spectrum fluctuates over time. For example, when looking at a small light source that fluctuates in a square wave cycle, the light source will be seen as a series of light spots that extend in space. (2) IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Definition in IEEE Std 1789-2015: ◎ "Brightness changes with time" (time modulation of light) ◎Contains all the above effects ◎Including visual effects and non-visual effects ▲Search results of non-flash lamps on a shopping platform Does the manufacturer's claim that there is no flicker really mean the aforementioned no flicker? It is important to note that if there is no indication of the test standard or result, the non-flicker they refer to may just mean that you can't see the flicker with the naked eye, which is different from what you think. At present, our country has made flicker related standards for desk lamps. According to the CQC1601-2016 "Technical Specification for Visual Work Desk Lamp Certification" implemented on 2016/11/02, flicker should comply with IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) IEEE Std 1789-2015 standard. In a document released by IEEE in 2015, the stroboscopic risk is divided into several levels. As shown in Figure 2, the green area covers the non-hazardous level, while the yellow area is low risk, exceeding the yellow part (white area). ) Is unacceptable. Table 1 and Table 2 list the low-risk and non-hazardous areas, the limit of the lamp flicker percentage (fluctuation depth). ▲Figure 2 IEEE Std 1789-2015 standard Under the AC frequency of 50Hz, the general domestic lamps' stroboscopic frequency is 100Hz, and the measured luminaire's stroboscopic percentage is less than 3.2%, which is the limit range of no stroboscopic hazard; of course, as long as the stroboscopic percentage is within the low risk range of 8%, Lamp strobe is in the safe range, if it is higher than 8%, the lighting product can be regarded as unsafe. We can clearly see in the previous chart that the light output waveform frequency f is a very important reference index. According to the calculation formula, whether it is less than the corresponding fluctuation depth limit, if it exceeds it, it does not meet its standard. In fact, "no flicker" is not really no flicker at all, but at a certain high frequency (as shown in Table 2, the light output waveform frequency f>3125Hz, high frequency immunity level) , has exceeded the human eye nerve response speed (The limit of the fluctuation depth of the non-hazardous impact level area), which will not damage the eyeball. There are also related testing institutions in China, such as the Electric Light Source Quality Supervision and Testing Center, which can test against the IEEE Std 1789-2015 standard (as shown in the test report in Figure 3). Because dimming is just another cause of flicker. When the lamp is loaded with dimming function, the stroboscopic flicker tends to be further intensified. Especially when the dimming is dark, the fluctuation depth is relatively large. Therefore, for lighting products that have a dimming function or claim to be connected to a dimming controller, at least their frequency should be measured when the dimming is the brightest (100% brightness) and the dimming is dark (20% or lower brightness). Flash performance. ▲Figure 3 Test reports of related testing institutions From the test results in Figure 4, under the maximum brightness, intermediate brightness, and minimum brightness detections, if the light output waveform frequency f>3125 Hz, that is, "exempt from assessment" (high-frequency exemption level), and achieve the strictness of no flicker Request . ▲Figure 4 Inspection report results of dimming lamps at three different brightnesses In the 2017 315 ​​International Consumer Rights Day Gala, the host and related technicians tested two LED eye protection lamps on site. In addition to the test data of the professional instrument, the technician also instructed the host to use a smart phone to perform the test. The result clearly saw the strobe, and said, "Just remember this trick: turn on the camera function of the phone and let the lens Quasi-light bulb, pay attention to the flickering on the screen, it is clear at a glance whether the strobe is serious!" In fact, it is true that you can see the strobe when shooting the lamp with the mobile phone camera, but this is not a way to judge whether the product is qualified. The main reasons are as follows: 1. What you see through the mobile phone screen is not what your eyes perceive directly; it is processed by the mobile phone's sampling circuit. -> An image with a rolling shutter effect. 2. The frequency of "sampling + display" of some mobile phones will be automatically adjusted within a certain range according to the light changes within the range of the camera. -> The sampling frequency is not high enough and not fixed! 3. The frequency, adjustment range and display mode of "sampling + display" of each mobile phone of different brands (related to the rolling door effect) may be different; ->Different mobile phones bring different measurement parameters of their own! 4. Some people may say that when there are no black stripes when measuring with a mobile phone, it means that the light waveform has not changed, which at least shows that the light is good. -> This may not be true! If the sampling frequency of the mobile phone is exactly the same as the light waveform, then the mobile phone will be deceived, telling you that the light is very good and there is no change! 5. Finally, the shutter of the phone will also affect your judgment. ->The shorter the shutter time, the more obvious the "stroboscopic" seen by the mobile phone, but the longer the shutter time the "stroboscopic" is likely to disappear. The mobile phone is not a stroboscopic detection tool, but it can be a reference tool. Since a modern mobile phone has one hand, it can be used to take pictures or photography anytime and anywhere. If the mobile phone is used under severe stroboscopic lights, it is very easy to find on the mobile phone screen that the ripple of light and dark affects the effect and quality of the shooting, so the mobile phone can Make a reference tool first. ▲The same lamp uses different dimming drivers, the lighting effects are obviously different To truly be able to detect flicker, professional testing equipment is still required (as shown in Figure 5), which can meet the requirements of many latest flicker measurement standards including IEEE, Energy Star, IEC, CIE, etc., and is suitable for laboratories and On-site measurement site. Individuals can also use a portable stroboscopic measuring instrument (Figure 6), which can also display important references for stroboscopic, such as "stroboscopic percentage" and "stroboscopic index". It also has an evaluation function that allows users to directly interpret the light. The quality is good or bad, such as: very serious, obvious existence, almost no, high frequency exemption, etc. ▲Figure 5 Light source stroboscopic measuring instrument ▲Figure 6 Evaluation of stroboscopic measuring instrument-no stroboscopic (high frequency exemption level) In recent years, the public’s calls and requirements for healthy lighting have become higher and higher. In order to effectively improve the quality of light, more and more consumers have learned about the potential damage caused by stroboscopic. The problem of stroboscopic must be faced with solve. However, there are still a large number of lighting manufacturers' lamps on the market that do not meet the "flicker-free" requirement. The final reason is that the selected LED driver does not meet the standard. Although there are relevant national standards for "No Flicker", it is not a mandatory requirement. Although a small number of manufacturers have launched so-called "No Flicker" products, they can effectively relieve everyone's doubts about stroboscopic because they cannot be visually judged. For this reason, lighting designers and lighting engineering companies have used stroboscopic measuring instruments to test whether they are up to the standard, and they have also heard that Party A and the final consumer prepare their own stroboscopic testing. Of course, the most effective way is to ask the manufacturer to provide a credible test report related to the test unit . Having a healthy light environment is the basic requirement. Choosing a good LED driver can minimize the negative impact of stroboscopic light. PCR Fluorescence Analyzer Filters
The fluorescence detection filter consists of a hard film. The fluorescent bandpass filter provided by our company achieves high signal-to-noise ratio, the background reaches 10-5-10-6, the excitation and emission filters are highly isolated, and the spectral characteristics are stable.
Applications: Fluorescent PCR detection, biochips, flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy and fluorophotometers.
NBPF:FWHM<15nm filter
BP: FWHM 15nm-40nm filter
WBP:FWHM >40nm filter
Specifications:
Substrate:BK7, Fused Silica etc. Pcr Fluorescence Analyzer Filters,Od6 Optical Filters,365Nm Bandpass Filters,Fluorescence Bandpass Filters Zoolied Inc. , https://www.zoolied.com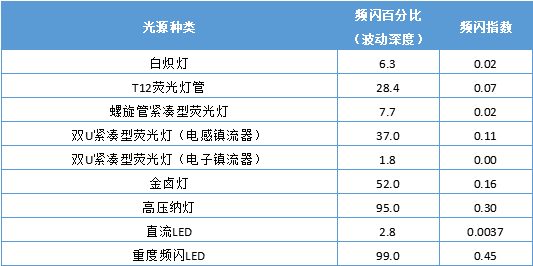







Filters can be customized according to user needs.
Size:D6-D25mm or Square
Blocking range: 200nm - 2000nm
OD4-OD6