The physical mechanism of graphene-doped carriers inducing RKKY to achieve spin-exchange between atoms and its modulation
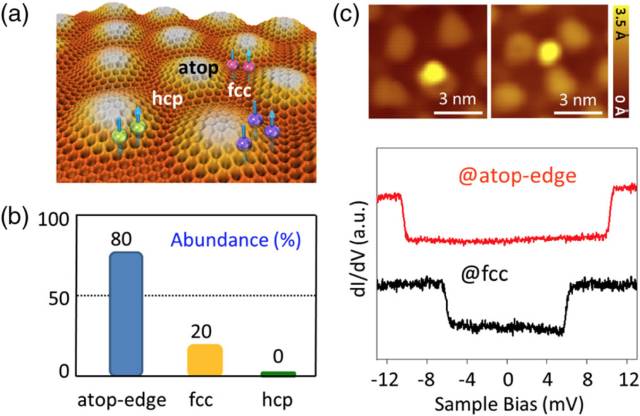
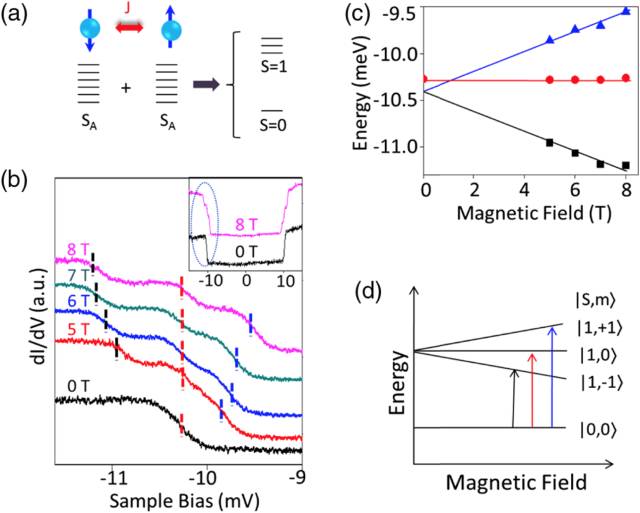
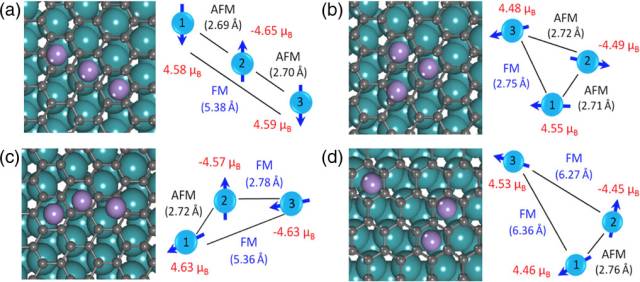
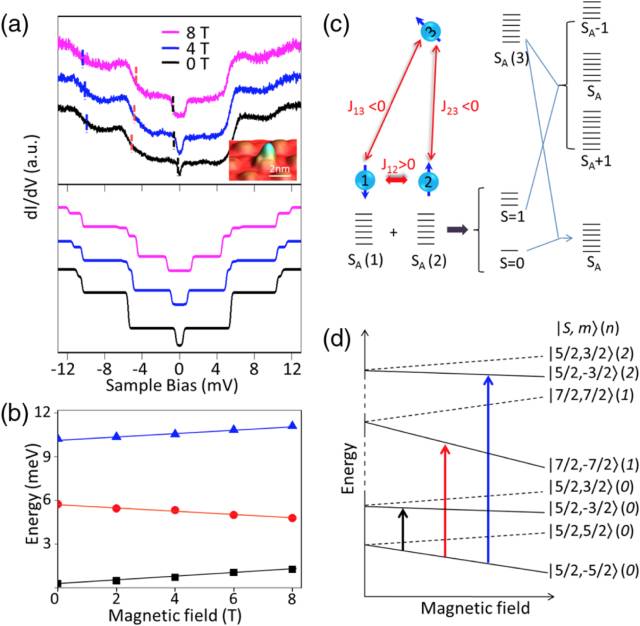
Nanoscale magnetic small clusters (composed of several atoms) are the basic unit for constructing nanomagnetic devices and spintronic devices, and are also ideal systems for studying the spin-exchange interaction between magnetic atoms. How to directly measure and study the spin coupling strength between two magnetic atoms at the atomic scale, and realize the regulation of its spin exchange is a very important basic problem. The difficulties and challenges in the experiment are mainly how to construct each other. A cluster of two or a limited number of magnetic atoms acting. The method of preparing magnetic atom clusters can usually only be achieved by epitaxial or etching methods on several limited substrate surfaces (usually metal or insulating substrates), but the structure is difficult to achieve precise control at the atomic scale. The controlled growth of magnetic atom clusters on weakly interacting substrates has been an important frontier topic in the study of spin-exchange between magnetic atoms. Graphene is an important class of spintronic materials, which has potential application value in non-rotating electronic devices. In recent years, the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences/Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics (Gao) Research Group has made a series of breakthroughs in the controllable growth and physical properties of high-quality graphene. They proposed a high-quality, large-area graphene growth technique based on single-crystal surface epitaxy. It is the first in the world to achieve a single-crystal graphene with a defect controllable on a Ru(0001) surface. Chin. Phys. 16, 3151 (2007); Adv. Mater. 21, 2777 (2009)], and conducted a series of studies on its physical properties and structural modulation [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 14136 (2009) Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 219701 (2010); J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 22, 302001 (2010) (Cover Story), Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 093101 (2012) (Cover story); 100, 083101 (2012); 102, 093106 (2013)]. Graphene epitaxially grown on the surface of Ru(0001) not only has large-area, high-quality characteristics, but also has a natural periodic Moiré superlattice structure, and electronic doping of graphene by metal substrate, Gao Hongjun Research Group The Kondo effect of a single magnetic cobalt atom was observed for the first time in experiments, and the control of the Kondo effect was achieved by using a molar superlattice [Nano Letters, 14, 4011 (2014)]. Recently, they used this graphene molar superlattice structure as a template to study the spin-coupling interaction between magnetic atoms. The research team's doctoral students, Jin Dong, Wu Xu, and Guo Haiming, used ultra-low temperature vector magnetic field scanning tunneling microscope/scanning tunneling (STM/STS) technology to base single-layer graphene on Ru(0001) single crystal. The in-situ low-temperature deposition technique is used to control the selective and selective adsorption of manganese clusters (dimers and trimers). The inter-atomic spin exchange between different manganese clusters is detected for the first time in experiments. Controllable modulation. The scanning tunneling spectrum of the dimer cluster formed by two manganese atoms exhibits an excitation step from the singlet ground state to the triplet ground state. After the application of the magnetic field, the step is three-stage splitting, and the two atoms are anti-iron. Magnetic coupling, the coupling strength is modulated by its adsorption position and interatomic distance at the graphene substrate. For the more complex manganese trimer cluster structure, multi-stage spin excitation is observed on the STS line and exhibits different magnetic field response characteristics. Combined with the Heisenberg spin model, the atoms are not collinearly arranged in the cluster. At the same time, information such as the type and intensity of spin coupling between atoms is obtained. When a manganese trimer having a triangular structure is formed, two of the manganese atoms form an antiferromagnetic coupling similar to the above dimer, and the third manganese atom and the other two manganese atoms form a ferromagnetic coupling. The research team's Ph.D. students Pan Jinbo, Zhang Yanfang and Du Shizhen, researcher Yang Yifeng from the Institute of Physics and Professor Ouyang Min from the University of Maryland, USA, conducted the first-principles and Heisenberg spin model theory calculations. The results show that graphene/ The difference in electronic structure between different regions of Ru's molar period is the main reason for affecting and modulating the antiferromagnetic coupling strength between manganese magnetic atoms. Further analysis found that in addition to the direct spin exchange between manganese atoms, there is a non-local Ruderman-Kittel-Kasuya-Yosida (RKKY) indirect exchange, which is related to the doping carrier concentration of the graphene substrate. . For the first time, this work directly modulates the spin interaction between magnetic atoms at the atomic scale. It verifies the physical mechanism of graphene-doped carriers to induce RKKY, and provides an atomic scale between the magnetic atoms. Spin coupling, and potential pathways for controlled self-assembly of different spin-type clusters. The relevant research results are published in Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 176806 (2017). This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology 973 (No. 2013CBA01600, 2013CB932901, 2016YFA0202300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11574363, 61274011, 61390501, 51325204) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Figure 1: A) Schematic diagram of manganese clusters adsorbed on graphene/Ru (0001) molar cycle structure; b) Statistics on the number of adsorbed manganese atom dimers at different positions of graphene molar cycle; c) Manganese at different adsorption sites The STM map of the polymer and the corresponding STS line. Figure 2: a) Schematic diagram of antiferromagnetic coupling in manganese dimer; b) Spin excitation spectrum of manganese dimer, showing spin-excited steps at zero field (0 T) in magnetic fields (5, 6, 7 and 8 Triple splitting occurs under T). c) The splitting energy (fitting from Figure b) increases as the strength of the magnetic field increases. d) Schematic diagram of the transition of the manganese dimer from singlet to triplet in a magnetic field. Figure 3: Four stable optimized configurations for the adsorption of manganese trimers on graphene/Ru calculated by DFT. According to the type of spin coupling between atoms, it can be divided into two categories: AFM-AFM-FM (a and b) and AFM-FM-FM (c and d). Figure 4: a) The spin excitation line (top) and the theoretical simulation line (bottom) obtained from the manganese trimer experiment (AFM-FM-FM model, where J12 = 8.9 meV, J13 = J23 = -1.3 meV, Comparison of D = -0.08 meV ). b) The relationship between the excitation step offset energy obtained from the experimental line of Fig. a as a function of the magnetic field strength. c) Schematic diagram of the energy level and degeneracy of the manganese trimer (AFM-FM-FM model). d) Schematic diagram of the transition of the manganese trimer from the ground state to the excited state under a magnetic field.
The 8-inch tablet will have a big impact on the 7-inch and 10-inch tablet market. Because the portability of an 8-inch tablet is stronger than that of a 10-inch tablet, and the usable area is larger than that of a 7-inch tablet. The most important thing is that the price is more moderate, which is much cheaper than a 10-inch tablet. It can be said that the 8-inch tablet computer has a good balance between portability and screen display area, and is more likely to be favored by the majority of users.
8 Inches Tablet Pc,Tablet Computer,8 Inch Android Tablets,8 Inch Tablet Jingjiang Gisen Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.jsgisentec.com