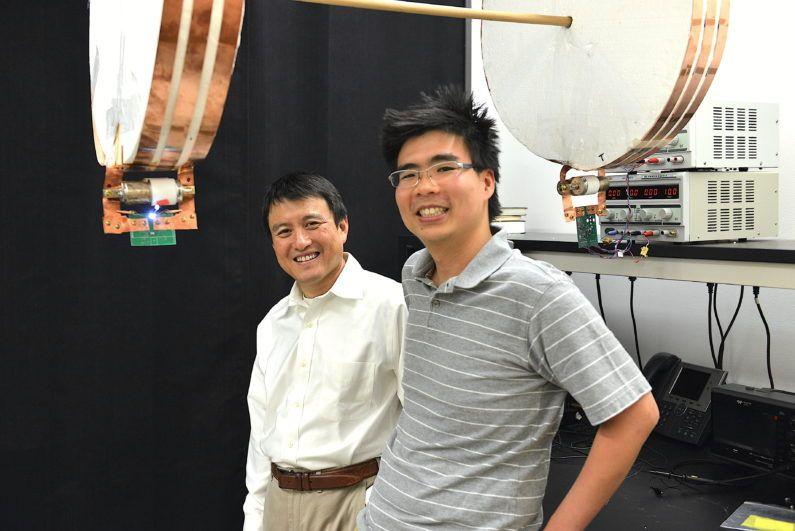
A giant step-by-step expert in electric vehicles researches "charging while driving"
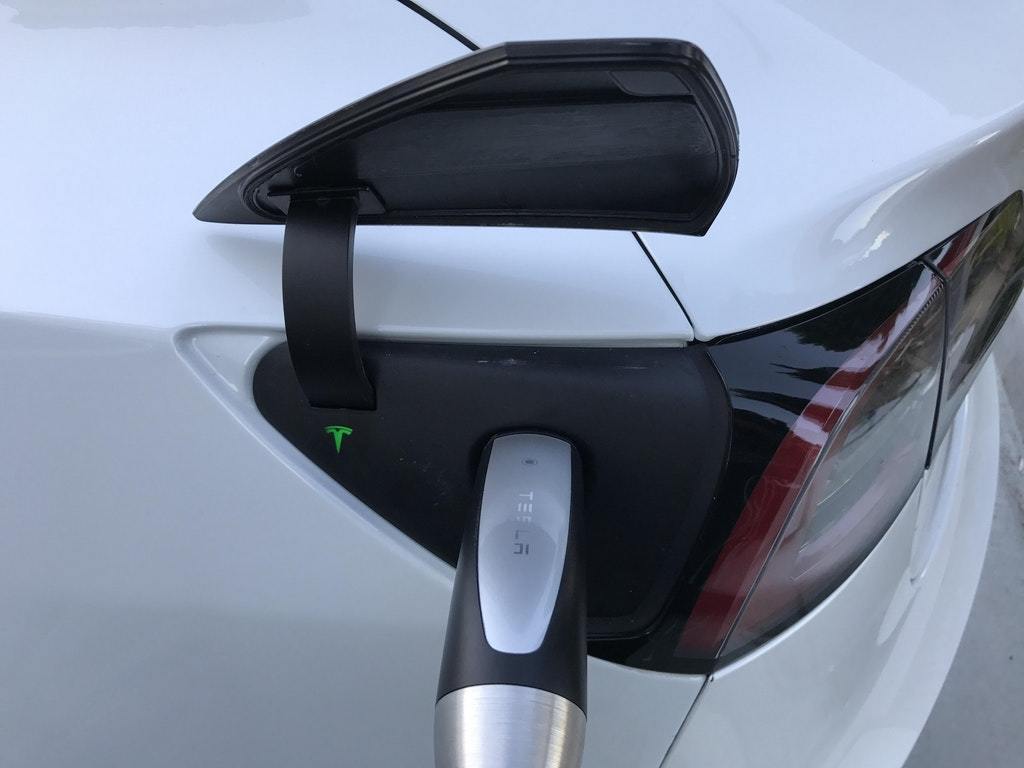
In a recent study, scientists at Stanford University used wireless charging to charge mobile light bulbs. This research and development technology can also make electric vehicles no longer limited to limited mileage, which is one of the biggest drawbacks of electric vehicles. If the electric car can be charged while driving on the highway, this can almost eliminate people's concerns about driving mileage, can also save costs, and perhaps make electricity become the standard fuel for cars. Now scientists at Stanford University have tackled a huge problem. In the future we can wirelessly transmit current to nearby moving objects. Scientists published their research results in a natural journal published on June 15. Stanford professor Shanhui焖an (left) and his graduate student Assawaworrarit have developed a device that can wirelessly charge objects at close range. This technology can be used to charge electric cars on the highway, for medical transplants, or to charge your phone while you walk. "In addition to developing wireless charging for cars and personal devices like mobile phones, our new technology can make robots no longer controlled by people. We are still trying to implement this idea," said Shanhui, professor of electrical engineering at Stanford University.焖an said. "We still need to drastically increase the amount of electricity needed to charge an electric vehicle, but we don't need to make the radio transmission too far." The team was developed on the basis of MIT's 2007 R&D technology, which uses radios to charge stationary objects several feet away. In this new study, the research team wirelessly charged a moving LED light bulb. The entire charging process requires only 1 milliwatt of power, while driving an electric vehicle usually requires 10,000 watts of electricity. The Stanford research team is currently working to significantly increase the power of wireless charging and adjust the system to remotely charge and increase charging efficiency. Car driving mileage Wireless charging will solve one of the major drawbacks of plug-in electric vehicles - limited driving range. Tesla Motors expects that the upcoming model will be charged up to 200 miles, while the listed Chevrolet pure electric vehicle, Bolt, has a range of 238 miles. But to fully charge the battery, electric cars usually need to charge for several hours. A car system that can be charged while driving can overcome these obstacles. Tesla Electric Vehicle Model 3 Fan explained: "In theory, this technology allows the driver to drive for unlimited hours without having to stop and charge the car. You can charge your electric car while driving on the highway." The coil on the bottom of the electric car can turn on the current through a series of charging coils buried in the road. Some transportation specialists have conceived an automated highway system that can be wirelessly charged by solar energy or other renewable energy sources. The goal of this vision is to reduce traffic accidents, drastically improve traffic conditions, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Wireless technology can also assist GPS navigation for driverless cars. GPS positioning can be accurate to 35 feet. For the sake of safety, driverless cars need to be located in the center of the lane. There, there are coils installed for the transmission of current, which can provide very accurate vehicle positioning for GPS satellites. Magnetic resonance The medium-range radio transmission developed by Stanford University and other universities is based on magnetic induction technology. Just as large power plants generate alternating current in coils between magnets, alternating currents through an oscillating circuit generate an oscillating magnetic field. This magnetic field can also cause the electrons in the nearby coils to vibrate for wireless charging. If the magnetic resonance frequency and direction of the two coils match precisely, the transmission efficiency of wireless charging will further increase. However, when the car is running, it must be controlled by humans so that the magnetic resonance frequency is the same, so as to guarantee a constant current. Therefore, the positions of the power transmission coils and the receiving coils need to remain unchanged, otherwise the circuit parameters need to be continuously adjusted, which is a complicated process. To meet this challenge, the Stanford University research team replaced the RF source in the power transmitter with a common voltage amplifier and feedback resistor. The system will automatically and accurately calculate the magnetic resonance frequency of different power transmission distances without human intervention. Assawaworrarit, the main participant in the study, said: “The installation of a voltage amplifier allows the power to efficiently transmit in most areas of the three-foot range, despite changes in the direction of the power receiver. This eliminates people’s access to the circuit. Continuous adjustment requirements." Assawaworrarit tested this method by placing an LED light bulb on the receiving coil. In the traditional case without tuning, the brightness of the LED light decreases as the receiver distance becomes longer. In the new device, the brightness of the LED lamp remains unchanged when the distance from the power receiver to the transmitter is approximately 3 feet. Fan's team recently submitted a patent application. The team used a general-purpose amplifier, which has a relatively low power supply efficiency of about 10%. They said that they can design amplifiers specifically tailored for wireless charging, which can increase the power supply efficiency to 90%. He said: “We not only need to wirelessly charge electric vehicles, but also apply this technology to some small devices or medical devices to make it do its best. For all products that can benefit from wireless charging, It's all important." [Selected from: futurism.com Author: Pixabay compile: NetEase see foreign intelligence platform Ke board under tiles on roof # compiler turn Po beer nuclear military / p>
ZGAR TWISTER Disposable
ZGAR electronic cigarette uses high-tech R&D, food grade disposable pod device and high-quality raw material. All package designs are Original IP. Our designer team is from Hong Kong. We have very high requirements for product quality, flavors taste and packaging design. The E-liquid is imported, materials are food grade, and assembly plant is medical-grade dust-free workshops.
Our products include disposable e-cigarettes, rechargeable e-cigarettes, rechargreable disposable vape pen, and various of flavors of cigarette cartridges. From 600puffs to 5000puffs, ZGAR bar Disposable offer high-tech R&D, E-cigarette improves battery capacity, We offer various of flavors and support customization. And printing designs can be customized. We have our own professional team and competitive quotations for any OEM or ODM works.
We supply OEM rechargeable disposable vape pen,OEM disposable electronic cigarette,ODM disposable vape pen,ODM disposable electronic cigarette,OEM/ODM vape pen e-cigarette,OEM/ODM atomizer device.
Disposable E-cigarette, ODM disposable electronic cigarette, vape pen atomizer , Device E-cig, OEM disposable electronic cigarette ZGAR INTERNATIONAL TRADING CO., LTD. , https://www.zgarpods.com