Talking about the Harmonic Problem of Smart Grid——The Development of Super Harmonics
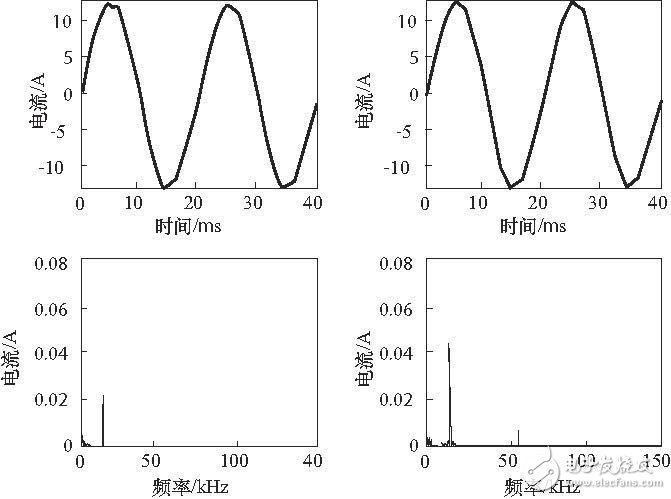
For super-harmonics, China has not carried out relevant research, but some effects have been detected. Based on recent foreign literatures, this paper briefly introduces the generation, impact, main characteristics and current research trends of superharmonics, for reference by relevant professionals, in order to carry out research in this area in China. 1, the generation of super harmonics Today, power electronics technology is still developing rapidly, and its application range is almost infiltrated into various fields. One of the important signs of the development of the technology is that the switching speed of the thyristor is greatly improved. For example, the switching frequency of the inverter (DC/AC converter) has been increased from the early tens of Hertz, several kilohertz to several tens of kilohertz or even several Hundred kilohertz. With the vigorous development of renewable energy, especially the investment of a large number of solar photovoltaic inverters (ie PV inverters), and the application of various switching power supplies, the grid (mainly in the low-voltage grid) is super in the range of 2 kHz to 150 kHz. Harmonics are rapidly increasing and the number of harmful effects is on the rise. In addition, the utility grid is generally used for signal transmission, and three types of signal systems are considered in the literature: 1) The power company's pulsation control system, the frequency range is 100Hz ~ 3kHz (generally less than 500Hz), under normal circumstances within 5% N, when there is resonance, up to 9%N. 2) The power carrier's power carrier, with a frequency range of 3 kHz to 95 kHz, allows a signal level of 5% N, and these signals decay quickly (greater than 40 dB) when transmitted in the grid. 3) The signal system of the end user (residential area or industrial user), such as Europe (ITU area 1), has a frequency range of 95 kHz to 148.5 kHz, and the allowable signal levels are 0.6% N or 5% N, respectively. In some countries, the upper frequency limit is 500 kHz and the signal level is allowed to be 2 mV to 0.6 mV. The frequency of these signals is quite in the super-harmonic range, so the super-harmonic source in the power grid is generated by various electronic devices, and is also generated by the communication devices used. 2, the characteristics of super harmonics Studies have shown that the transmission dispersion of harmonics from 2 kHz to 150 kHz is different from ordinary harmonic emission, which is a new type of power quality phenomenon. One of the features is the so-called primary emission and secondary emission. The primary emission refers to the emission caused by the disturbance source (device) alone; the secondary emission refers to the emission of the disturbance source (device) after the other device transmits it. The two are significantly different. The main factors affecting the primary emission are: 1 topology of the device; 2 impedance of the connection point; 3 resonance. In a low-voltage network, the connection point impedance of the device consists of a transformer, a cable (referred to as the "impedance of the network"), and the internal wiring of the building, along with other connected device impedances, which can be referred to as the impedance of the facility, between 2 kHz and 150 kHz. In the frequency range, the network impedance is mainly inductive, which is relatively higher than the facility impedance (often based on the capacitance of the connected device). The main factors affecting the secondary emission are: 1 the emission intensity of the neighboring device; 2 the relationship between the device connection point impedance and the network and the facility impedance. Figure 1 is a measured waveform of the primary and secondary emissions of a television (TV) to a PV inverter. The main harmonic frequency generated by the PV inverter is 16 kHz. When the TV is connected, the secondary emission of the PV inverter is significantly amplified at 16 kHz; in addition, the 55 kHz line appears, and the latter does not appear in the native emission. TV generated. The test also found that the higher the superharmonic frequency, the closer the transmission distance: the 16 kHz component level produced by the PV inverter remains fairly stable at the connection point in the test house, slightly lower at the common connection point (PCC), The voltage or current component of 55 kHz to 150 kHz generated by other devices in the house is not detected at the PCC, which means that these frequency components are only transmitted between the indoor appliances and do not enter the power grid. This is another feature of super harmonics. Figure 1 Effect of a TV on the primary and secondary emissions of a PV inverter Yuchai 76-200KW Diesel Generator Yuchai 76-200Kw Diesel Generator,Yuchai 200Kw Generator,Yuchai Engine Generator,Diesel Generator With Yuchai Engine Shanghai Kosta Electric Co., Ltd. , https://www.ksdpower.com