Retrieve how to take up too much hard disk space
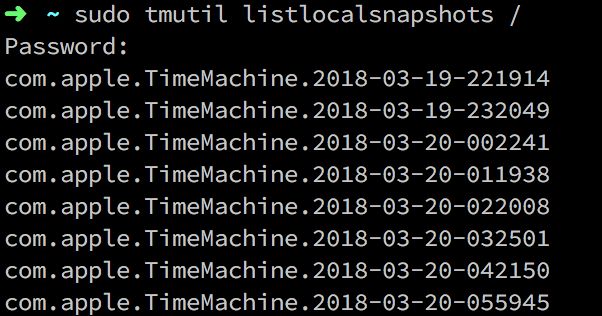
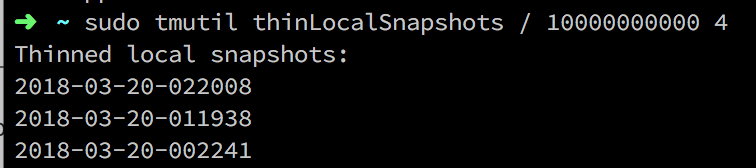
I have been working on files in my various electronic devices for the past two days. It’s useless to delete, other things put in a position or something. Tossing all day, when I wanted to see how many things were deleted, I found a strange phenomenon. The remaining space on my hard drive has become very small, even worse than before the cleanup, and the largest space, it turned out to be "system." The 223G that is written above is very strange, and the remaining space that can be used is actually less than 20G. â–File system error When encountering such an unusually large thing, the first thing that comes to mind is the file system error. A year ago, my computer had a similar situation, which was caused by a file system error, but the expansion was "other", and this time it was "system." So I rebooted into Recovery (press ⌘Command-R while booting) to run the disk tool for first aid. For system disks, first aid can only be resolved in Recovery to resolve certain issues. â–Application data retention In previous versions of the system, "other" was particularly large and it was unclear why most of the cases were due to this. In macOS, applications typically store their own data in ~~Library/Application Support, which is not automatically deleted when the application is deleted. The purpose is to allow you to continue to use the software in the previous state, but macOS has been unrestrained in this matter, making a lot of software a lot of files. If you have a lot of thoughts on your computer, you can try to clean it manually. Although CleanMyMac can clean up a lot of caches here, there are a lot of leaks. I deleted five or six pretty big folders, but none of them can be as big as 200G. â–Local snapshot Local snapshots are an early feature. In APFS, when you modify the hard disk, the file system will back up the modified files to generate some snapshots. These files do not take up too much space under normal circumstances, because they will be deleted by the system after 24 hours. But if you delete or modify too many files in a day, this will happen. Although Apple claims that these files will be automatically deleted when there is not enough space, these are real space footprints. If the space you need to perform now is larger than the current available space (such as installing Boot Camp), you will report an error directly. So mastering the method of clearing local snapshots can help you solve problems at critical times. How to clear local snapshots In versions prior to macOS 10.13, files were stored in the /.MobileBackups folder and can be removed directly. You can also turn off the local snapshot feature by running sudo tmutil disablelocal in the terminal. But after 10.13, APFS brought the local snapshot to the bottom layer, and the storage location of the snapshot file is actually in another partition! (Related to the container format feature of APFS) So you can't manually delete these files, and the above mentioned command to close the local snapshot has also been removed by Apple. So in APFS, we need more complicated steps to clean up these files. First enter the following command in the terminal to list the snapshot. Sudo tmutil listlocalsnapshots / The figure shows the list of snapshots currently on the local disk. To delete them, you can delete them one by one or delete them all. The command to delete a single snapshot is: Sudo tmutil deletelocalsnapshots [Date] When using, replace [Date] here with the date number in the above picture. Note that only the date is copied, such as: Sudo tmutil deletelocalsnapshots 2018-03-19-055945 Bulk deletion is more complicated. Apple does not provide a command to delete all snapshots. It only provides another command to delete the specified size snapshot: Thinlocalsnapshots / [purge_amount] [urgency] Among them, [purge_amount] to fill in the size of the deletion, in Bytes, [urgency] to fill the degree of extrusion, ranging from 1 to 4, will use a different cleaning scheme. For the purpose of deleting all of us here, we directly set the size to be deleted to 100G, and the degree of squeezing is 4. The command is: Sudo tmutil thinLocalSnapshots / 100000000000 4 It takes a certain amount of time to run, and a 100G snapshot will be eliminated after successful execution. There is a 0 in the picture, don't mind. Next, try to list the snapshots. If there are more than one, then it should be cleaned up to three times. At this time, open the machine again, you can see that the space has been released. What is a local snapshot Local snapshots are part of the Mac file protection mechanism. The backup of a Mac is mainly composed of three parts: Time Machine file version Local snapshot First of all, everyone is very familiar with it. Time Machine is a scheduled backup. After a fixed time, an incremental backup is performed. The backup location must be another partition. It will be saved until the target disk is not full. The second file version will save the most recently modified version of the file in /.DocumentRevisions-V100 when modifying the file, but file format support is required. The backup shares the available space with this partition and will continue to save until it reaches the limit. Sometimes some video files are stored in the old version, which will lead to a lot of space, but fortunately this thing is easier to clean up, and a lot of software can do it. The local snapshot is compared to the lower layer. For all file modifications on the disk, the local snapshot is backed up, and the backup shares the available space with the partition. In addition to the difference between the file version and the file version, it can also recover the formatting of the disk. However, this backup is only kept for 24 hours, which means that the mechanism exists only as an accident prevention measure before backup to Time Machine. So clearing local snapshots is generally without any risk. â– Some å” å¨ Whether it is the "other" that has plagued Mac users or the current "system", there is a problem that Apple is very unclear about the use of its own disk. I personally think it is very necessary to clearly indicate the volume occupied by the backup in the chart. Otherwise, a disk snapshot such as a local snapshot that changes frequently and has such a large extent will affect the user's judgment on the remaining space of the hard disk. This disk space chart becomes meaningless. Since the local snapshot feature is now directly integrated into APFS, it is no longer able to be shut down, and Apple has not provided a convenient solution to clean up these files, hoping to have an elegant solution in the future. Bitcoin mining machines are one way to obtain bitcoins. Bitcoin is an online virtual currency created by open-source peer-to-peer software. Instead of being issued by a specific currency institution, and produced by the massive computation of a specific algorithm, the Bitcoin economy uses a distributed database of nodes throughout the P2P network to identify and record all transactions. The decentralized nature and algorithm of P2P can ensure that it is impossible to artificially manipulate the value of bitcoin by producing a large number of coins.
Any computer can become a mining machine, but the returns will be low, and it may not mine a single bitcoin in a decade. Many companies have developed specialized Bitcoin mining machines with special mining chips that are tens or hundreds of times faster than normal computers.
Currency system by the user (the user through the key control wallet), trade (trade will be broadcast to the whole currency network) and miners (generated by competition calculation agreed on each node of the chain block, block chain is a distributed public authority books, contains the currency network of all the transactions happened) Bitcoin Mining Machine,Antminer S19j Pro,bitcoin Miner,btc mining machine,S19 Pro Hyd Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ylhm-tech.com

Bitcoin miners manage the Bitcoin network by solving the problem of proof-of-work mechanisms with a certain amount of work -- confirming transactions and preventing double payments. Because hashing is irreversible, finding the number of random adjustments required to match is difficult, requiring a trial-and-error process that can predict the total number of times. This is where the proof-of-work mechanism comes into play. When a node finds a solution that matches the requirement, it can broadcast its result to the whole network. Other nodes can then receive the newly solved data block and check whether it matches the rule. If the other nodes calculate the hash value and find that the requirement (the operation goal required by Bitcoin) is satisfied, then the data block is valid and the other nodes accept the data block.
Bitcoin Mining Machine:S19 Pro Hyd Asic Miner,S19 Pro Hyd Antminer Bitmain,S19 Hyd Bitmain Antminer,s19j pro antminer bitmain,whatsminer m50s,etc.