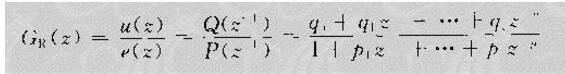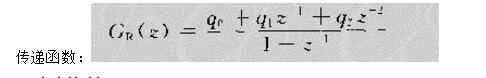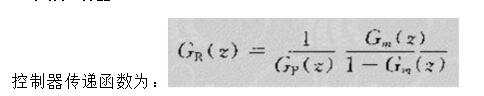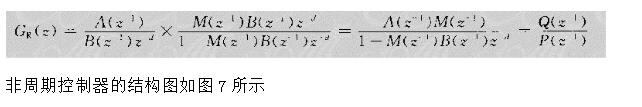Adaptive control of commonly used controllers _ adaptive controller simulation
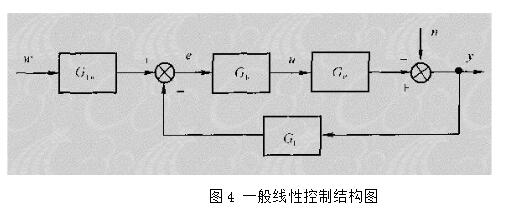
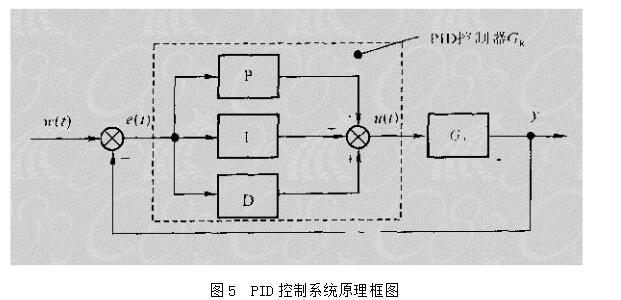
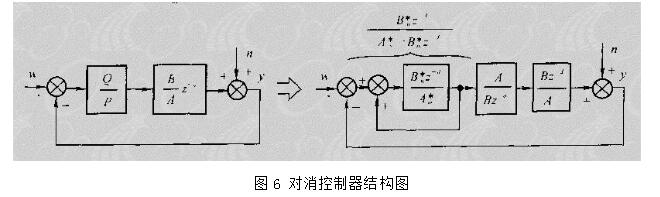
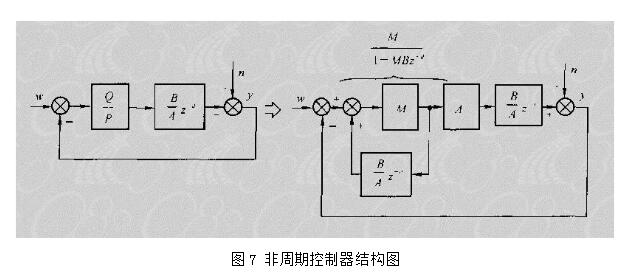
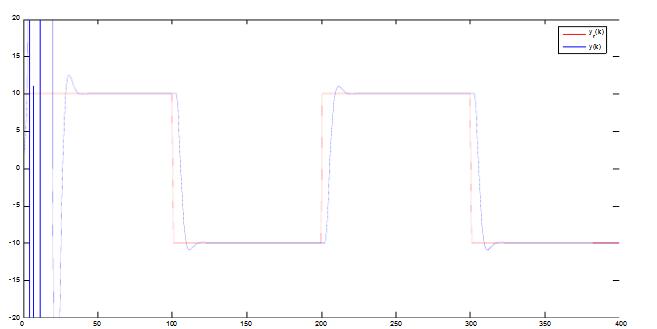
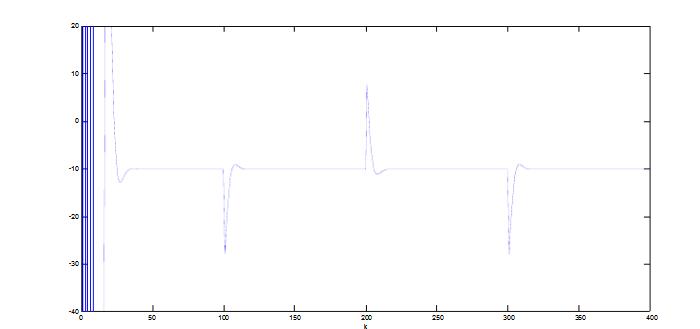
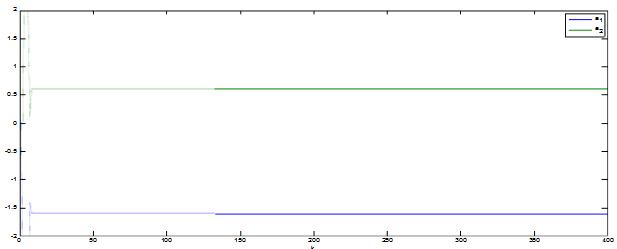
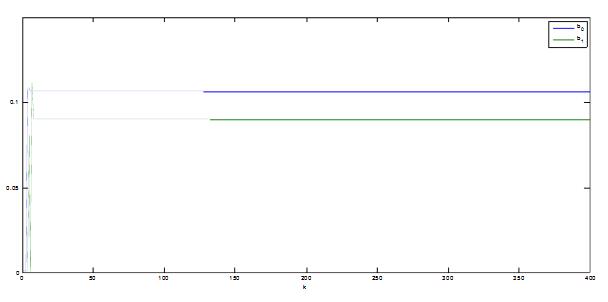
With the development of power electronics, microelectronics and information technology, AC motor drive control technology has also developed rapidly. The general development trend of modern AC drive control systems is intelligent, modular, digital and high frequency. Motor control technology has entered a new stage of development characterized by the application of modern control theory. In everyday life, adaptation refers to a feature in which a living organism can change its habits to adapt to a new environment. Therefore, intuitively, an adaptive controller should be a controller that can modify its characteristics to accommodate changes in the dynamics of objects and disturbances. The research object of adaptive control is a system with a certain degree of uncertainty. The so-called "uncertainty" here refers to the mathematical model describing the controlled object and its environment is not completely determined, including some unknown factors and random factors. Any actual system has varying degrees of uncertainty, sometimes manifested within the system and sometimes outside the system. From the inside of the system, the structure and parameters of the mathematical model describing the controlled object are not necessarily known to the designer in advance. The effect of the external environment on the system can be represented equivalently by many perturbations. These disturbances are usually unpredictable. In addition, there are some uncertainties in the measurement that enter the system. Faced with the various uncertainties of objective existence, how to design appropriate control effects, so that a specified performance index is achieved and maintained optimal or approximate optimal, this is the problem that adaptive control should solve. Adaptive control, like conventional feedback control and optimal control, is also a mathematical model-based control method. The only difference is that the prior knowledge of the model and disturbance based on adaptive control is relatively small and needs to be run in the system. In the process, the information about the model is continuously extracted, and the model is gradually improved. Specifically, the model parameters can be continually identified based on the input and output data of the object. This process is called online recognition of the system. As the production process continues, through online identification, the model will become more and more accurate and closer to reality. Since the model is constantly improving, it is clear that the control function based on this model will continue to improve. In this sense, the control system has a certain adaptability. For example, when the system is in the design stage, because the initial information of the object characteristics is relatively lacking, the system may not perform well when it is first put into operation, but as long as it runs after a period of time, after online identification and control, the control system gradually adapts. And finally adjust itself to a satisfactory working state. For example, some control objects may have large changes in their characteristics during operation, but the system can gradually adapt by identifying and changing controller parameters online. The conventional feedback control system has certain suppression ability for the changes of the internal characteristics of the system and the influence of external disturbances. However, since the controller parameters are fixed, when the internal characteristics of the system change or the external disturbance changes greatly, the system Performance often drops dramatically or even becomes unstable. Therefore, adaptive control is appropriate for a class of systems where the characteristics of the object or the perturbation characteristics vary widely, while at the same time requiring high performance indicators to be maintained frequently. However, it should also be pointed out that adaptive control is much more complicated and costly than conventional feedback control, so it is only considered when conventional feedback is not used to achieve the desired performance. The controller is an important foundation of the adaptive control system and an important link to achieve the established control strategy and guarantee the control performance. The following describes the control methods of several controllers based on linear theory. The structure of the linear control is shown in Figure 4. Gf pre-filter; Gk forward channel controller; Gp controlled process (object) Gz feedback link controller; n output interference; u control signal; R reference input; y system output 1, the general linear controller A general controller can be described as: 2, PID controller The PID controller is a linear controller with a fixed structure. The schematic diagram is shown in Figure 5. 3, the cancellation controller The structure of the controller is shown in Figure 6. The transfer function controlled by the aperiodic controller is: Other controllers predict controllers, minimum variance controllers, generalized predictive controllers, state controllers, state observers, and Kalman filters and caution controllers. Taking self-correcting PID control as an example, the self-correcting PID control is essentially a pole placement method, which is to adjust the structure and parameters of the PID controller to make the characteristic polynomial of the closed-loop system into a predetermined formula. The PID control expression is far from the original PID expression. Self-correcting discrete PID control. The output reference is compared to the actual output: Enter the initial value u: Parameter estimate a: Parameter estimation b It can be seen from the figure that the output of the self-tuning PID control process is basically consistent with the output of the reference model, and it can be seen that the system has achieved good control effects. Shenzhen Xcool Vapor Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.szxcoolvape.com