What is the Turing test _ Detailed explanation of the working principle of the Turing machine
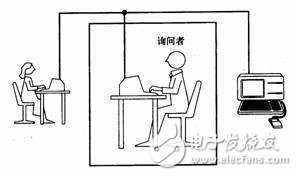
The Turing test was invented by Alan Messon Turing, which means that the tester is separated from the testee (one person and one machine) by some devices (such as a keyboard). The tester asks questions at will. After multiple tests, if more than 30% of the testers are unable to determine whether the testee is a human or a machine, then the machine passes the test and is considered to have human intelligence. The word Turing test comes from a paper written in the 1950 book "Computers and Intelligence" by Alan Messon Turing, a pioneer in computer science and cryptography. 30% of them are Turing's machine thinking in 2000. A prediction of ability, we are far behind this prediction. Turing proposed a way to test whether a machine has human intelligence. That is to say, a computer is very fast, the memory capacity and the number of logical units exceed the human brain, and many intelligent programs are written for this computer, and a large amount of data of a suitable kind is provided. Can you say that this machine has the ability to think? Turing is sure that the machine can be thinking, It is very difficult to distinguish whether an idea is "self-created" or a well-designed "imitation". Any evidence of self-created thought can be rejected. Turing tried to solve the long-standing philosophical debate about how to define thinking. He proposed a subjective but operational standard: if a computer has the same (act), react, and interact as the conscious individual. Then it should be considered conscious. In order to eliminate the prejudice in the human mind, Turing designed a "imitation game" that is the Turing test: the human tester in the distance judges the response of the two entities to various questions raised by the two entities within a specified period of time. It is human or computer. Through a series of such tests, the degree of success of computer intelligence can be measured from the probability that a computer is misjudged as a person. Turing predicts that at the end of the 20th century, computers will surely pass the "Turing test." On June 7th, 2014, at the "2014 Turing Test" conference held by the Royal Society, the host of the University of Reading, UK, issued a press release claiming the artificial creation of the Russian Vladimir Veselov. The intelligent software Eugene Goostman passed the Turing test. Although "Eu Jin" software is far from "thinking", it is also a landmark event in artificial intelligence and even in the history of computers. Pc Power Supply,Gold Pc Power Supply,Desktop Power Supply 650W,Psu Computer Power Boluo Xurong Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.greenleaf-pc.com Turing test he also defined the intelligence problem from the perspective of behaviorism, and thus proposed a hypothesis: a person does not touch each other, through a special way, and a series of questions and answers with the other party, If, for a long time, he can't judge whether the other person is a person or a computer based on these questions, then he can think that this computer has the same intelligence as the same person, that is, this computer can think. This is the famous "Turing TesTIng". At the time, there were only a few computers in the world, and almost all other computers could not pass this test.