Heat exchanger function in refrigeration system
Refrigeration system Refrigeration principle of a general refrigerator The function of the compressor is to compress the lower pressure steam into a higher pressure steam, so that the volume of the steam is reduced and the pressure is increased. The compressor draws in the lower pressure working fluid vapor from the evaporator, causes the pressure to rise, and then sends it to the condenser, which is condensed into a higher pressure liquid in the condenser, and becomes a pressure after being throttled by the throttle valve. After the low liquid is sent to the evaporator, it absorbs heat in the evaporator and evaporates to become a lower pressure steam, which is then sent to the inlet of the compressor to complete the refrigeration cycle. Heat exchanger heat exchangers (also known as heat exchangers or heat exchange equipment) are devices used to transfer heat from hot fluids to cold fluids to meet specified process requirements. They are an industry of convective heat transfer and heat transfer. application. Heat exchangers can be classified in different ways. According to its operation process, it can be divided into three types: partition type, hybrid type, and regenerative type (or regenerative type); according to the compactness of its surface, it can be divided into two types: compact and non-compact. Heat exchanger function in refrigeration system When the compressor refrigeration system uses hydrocarbons and NH3 as the refrigerant, the hydrocarbon and ammonia refrigeration systems use an indirect cooling system to solve the NH3 refrigeration compared to the direct expansion refrigeration system using HFC and R22 refrigerants. The toxicity of the agent, the flammability of the hydrocarbon refrigerant, the refrigeration system referred to herein generally refers to a commercial refrigeration system, and the refrigeration temperature is low. In the small and medium capacity range, the application of air conditioning chillers (indirect cooling systems) has become more common, in which cold water is secondary refrigerant, which uses the sensible heat change of water to deliver cooling capacity. The quick freezing cold storage hydrocarbon and the ammonia refrigeration system should adopt the indirect cooling system, and the secondary refrigerant circulation problem must be well solved, because the viscosity of the secondary refrigerant increases greatly as the evaporation temperature decreases, and the pressure loss of the cyclic process increases. It is bound to increase the power consumption of the circulating pump, resulting in a reduction in the COP of the entire system. Regarding the secondary refrigerant, the cold transfer is generally achieved by means of the sensible heat change of the solution, and the phase change mode, such as the excellent thermal performance of CO2, is used to realize the phase change process, and the CO2 is actually the second refrigeration. Agents, great progress has been made in this regard. There is no condensation process in the heat exchange process in the CO2 compressor outlet cooler. The internal heat exchanger uses the steam at the outlet of the evaporator to further cool the CO2 on the high pressure side. This internal heat exchanger is necessary, otherwise the COP value of the entire system will be low. The main functions of the low pressure liquid separation P recovery unit include: allowing a certain amount of liquid to enter the evaporator to simplify the control system and enhance heat transfer, ensuring that the system maintains a sufficient amount of liquid under various operating conditions or compensates for the reduction due to leakage. Quality, through capillary or throttle adjustment to ensure a sufficient amount of lubricant into the compressor, providing sufficient gas phase space to prevent overpressure during system shutdown.
Rectangular I/O Connectors
Antenk develop and specify high-performance I/O's throughout a wide variety of industries. These include SAS, SATA, PCIe, HSSG, FIBRE CHANNEL, INFINIBAND, IEC, CEA, IEEE, VESA, USB and many more.
I/O Connectors Application
Antenk can deliver standard and custom options of the following I/O connectors:
I/O Connectors General Specifications
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Rectangular Connector,Rectangular I Connectors,Rectangular O Connectors,Male Connector Rectangular,I/O Connectors,Input/Output Connectors ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.coincellholder.com
Antenk offers an expansive product line of I/O connectors including USB, HDMI, D-Sub, Modular Jacks, SFP, QSFP+, CXP, iPass+, iPass+ HD and more. In addition to standard I/O connectors and matching cable assemblies.Except a comprehensive range of standard Input/Output connector solutions for high-speed electronic data communication, Antenk engineers can design customized solutions. This extensive selection of I/O connectors and matching cable assemblies includes numerous next-generation solutions.All of our I/O connectors feature a variety of orientation options, as well as PCB and cable mount offerings.
Consumer / PC Products
Networking / Telecommunications Products
Mobile Products
Industrial Products
1394 Connector
Centronic Connector
D-Sub Connector
DVI Connector
Display Port Connector
HDMI Connector
Half Pitch SCSI Connectors
USB Connector
V.35 Connector
OBD Connector
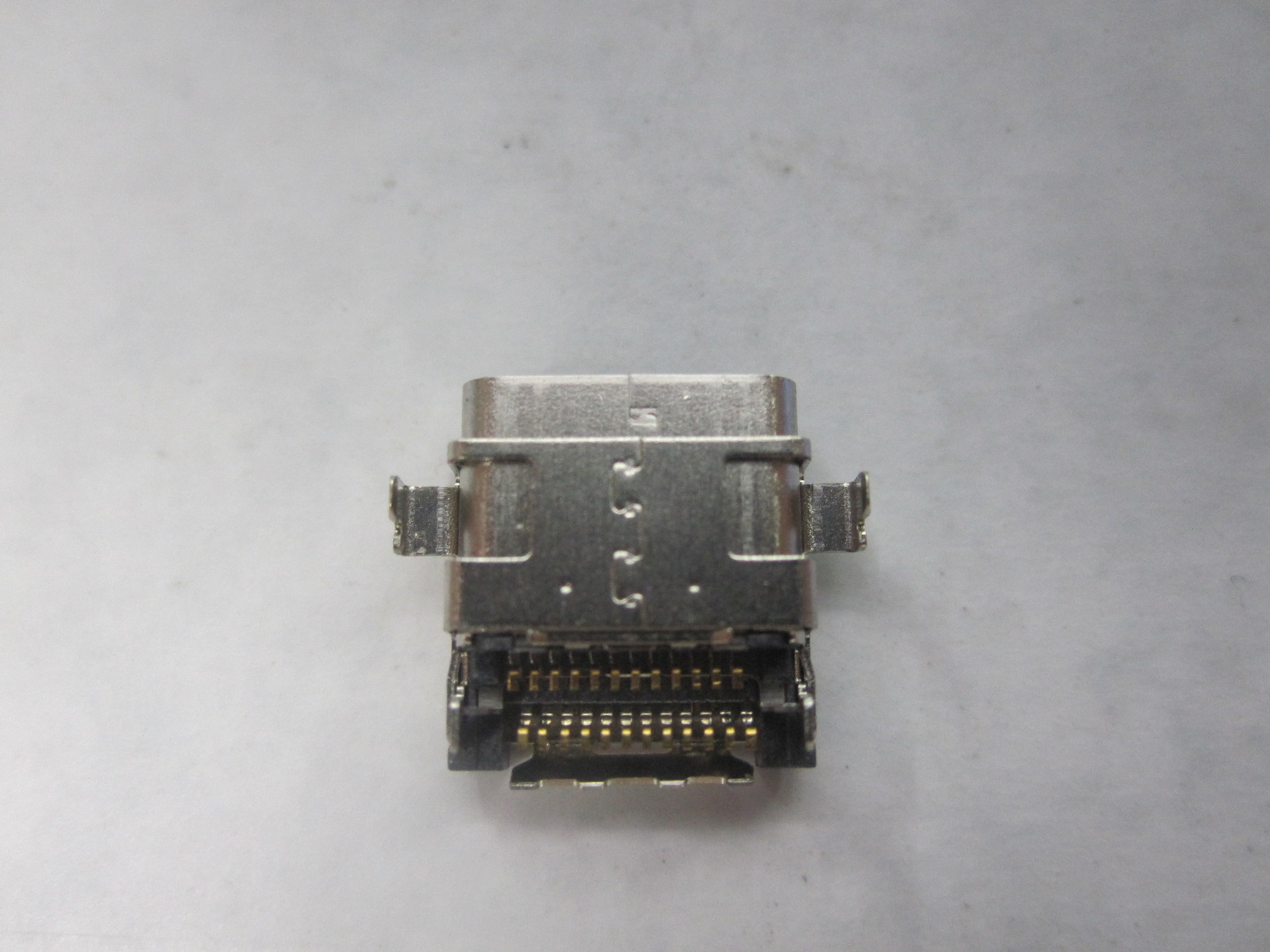


Contact Current Rating:5Amperes.
Dielectric Withstanding.
Dielectric Withstanding Voltage:AC 1000Vr.m.s.
Insulation Resistance:500 Megohms Minimum at DC500V.
Contact Resistance:25 Milliohms Maximum.
Operating Temperature:-55℃~105℃.

MATERIALS:
Contacts:Brass.
Insulator:PBT,UL94V-O Rated.
Shell:Cold Rolle Steel.
Metal Watertight Frame:PBT,UL94V-0.
O-Ring:Silicone.
NOTE:
Position:09PIN,15PIN,25PIN,37PIN.